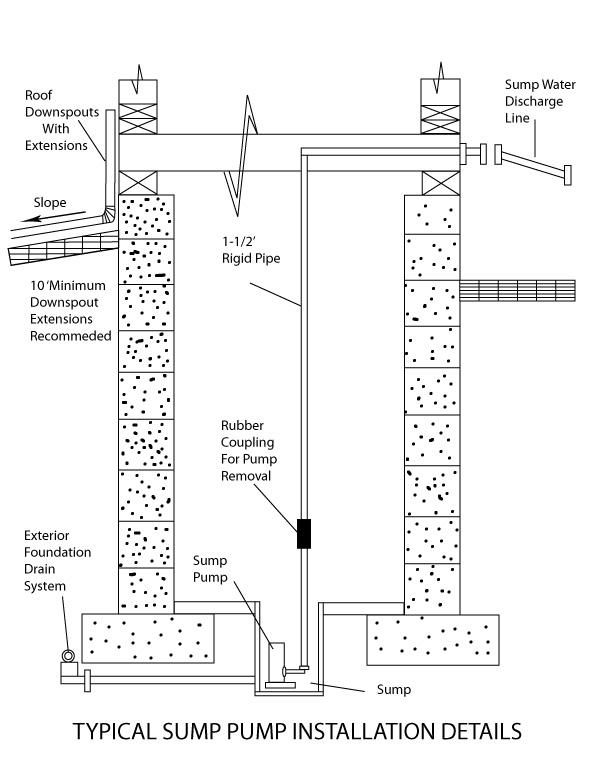
 A sump pump is a pump used to remove water that has accumulated in water collecting sump basin, commonly found in the basement of homes. The water may enter via the perimeter drains of a basement waterproofing system, funneling into the basin or because of rain or natural ground water, if the basement is below the water table level. Sump pumps are used where basement flooding happens regularly and to remedy dampness where the water table is above the foundation of a home. Sump pumps send water away from a house to any place where it is no longer problematic, such as a municipal storm drain or a well. A wet basement is most often caused by water build up in the soil around your home’s foundation. From there the water enters though the cracks and pores of the basement walls and floors. The keys to keeping your basement dry is to prevent water from getting in (basement waterproofing), controlling the humidity levels (dehumidification), and remove any water that finds its way into your basement (sump pump).Sump pumps are installed in the lowest section of the basement and will pump out any water that has entered the basement before it starts flooding the basement floor. As groundwater makes its way into the basement, it is diverted into the sump pit or sump basin. When the water in the pit reaches a certain level, the sump pump turns on and begins to pump it out. The water flows out of the house through a discharge pipe and is discharged away from the home’s foundation. Usually hardwired into a home’s electrical system, sump pumps may have a battery backup. The home’s pressurized water supply powers some pumps, eliminating the need for electricity at the expense of using potable water, potentially making them more expensive to operate than electrical pumps and creating an additional water disposal problem. Since a sump basin may overflow if not constantly pumped, a backup system is important for cases when the main power is out for prolonged periods of time, as during a severe storm.
A sump pump is a pump used to remove water that has accumulated in water collecting sump basin, commonly found in the basement of homes. The water may enter via the perimeter drains of a basement waterproofing system, funneling into the basin or because of rain or natural ground water, if the basement is below the water table level. Sump pumps are used where basement flooding happens regularly and to remedy dampness where the water table is above the foundation of a home. Sump pumps send water away from a house to any place where it is no longer problematic, such as a municipal storm drain or a well. A wet basement is most often caused by water build up in the soil around your home’s foundation. From there the water enters though the cracks and pores of the basement walls and floors. The keys to keeping your basement dry is to prevent water from getting in (basement waterproofing), controlling the humidity levels (dehumidification), and remove any water that finds its way into your basement (sump pump).Sump pumps are installed in the lowest section of the basement and will pump out any water that has entered the basement before it starts flooding the basement floor. As groundwater makes its way into the basement, it is diverted into the sump pit or sump basin. When the water in the pit reaches a certain level, the sump pump turns on and begins to pump it out. The water flows out of the house through a discharge pipe and is discharged away from the home’s foundation. Usually hardwired into a home’s electrical system, sump pumps may have a battery backup. The home’s pressurized water supply powers some pumps, eliminating the need for electricity at the expense of using potable water, potentially making them more expensive to operate than electrical pumps and creating an additional water disposal problem. Since a sump basin may overflow if not constantly pumped, a backup system is important for cases when the main power is out for prolonged periods of time, as during a severe storm.
Sump Pumpilaos2023-06-16T16:03:40-04:00

Stay In Touch